In the ever-evolving world of technology, drones have emerged as one of the most fascinating and versatile inventions of our time. From soaring through the skies and capturing breathtaking aerial footage to delivering packages right to our doorsteps, drones have revolutionized various industries and opened up a world of possibilities. As we dive into 2024, the uses and different types of drones continue to expand at an astonishing rate, shaping the future in ways we never imagined possible.
What Is A Drone?
Drones come in various shapes and sizes, each designed with specific capabilities to serve different purposes. The diversity in drone types is vast, From fixed-wing drones resembling miniature airplanes to quadcopters with four rotors for enhanced stability.
By exploring the unique characteristics of each type, users can harness the full potential of drones for tasks ranging from photography and videography to agricultural surveys and search-and-rescue missions.
What Are The Different Types Of Drones And Their Uses?
There are various types of drones, each designed for specific purposes. We discuss by breaking them into drone categories:
According To Wing Types
Following are the different drones according to wing types:
| Drone type | Single-rotor helicopter drones | Multi-rotor drones | Fixed-wing drones | Fixed-wing hybrid VTOL drones |
| Pros | 1. Increased Aerodynamics 2. Greater Stability | 1. Suitable for a variety of environmental operations 2. Lower cost 3. Convenience to drone pilots | 1. Higher payload capacity 2. Able to cover large areas 3. Faster | 1. Can hover in place for extended periods of time 2. Cruise for long periods of time 3. Fly at high speeds 4. Cover large areas |
| Cons | 1. More dangerous 2. Harder to fly, more training needed 3. Expensive | 1. Unable to work in harsh environments 2. Short flight time | 1. Require a larger take-off and landing space 2. Can’t hover 3. Often more expensive 4. More complex to operate | 1. Expensive 2. Not as efficient as either the basic fixed-wing or rotary-wing configurations |
| Uses | 1. Aerial photographs 2. Monitor property, and inspect hard-to-reach areas | 1. Aerial photography 2. Aerial inspection 3. Landing surveying | 1. Surveying and mapping 2. Progress monitoring 3. Safety inspections 4. Volume calculations | 1. Aerial mapping 2. Utility inspection 3. Surveillance 4. Agriculture |
Single-rotor Helicopter
It is the type of drone with solid abilities. Unlike multi-rotor drones that use batteries, they use gas engines for longer flights and heavier loads. This makes them great for long surveillance missions or lifting heavy things. But, their big blades make them riskier to fly, and they need skilled and careful pilots.
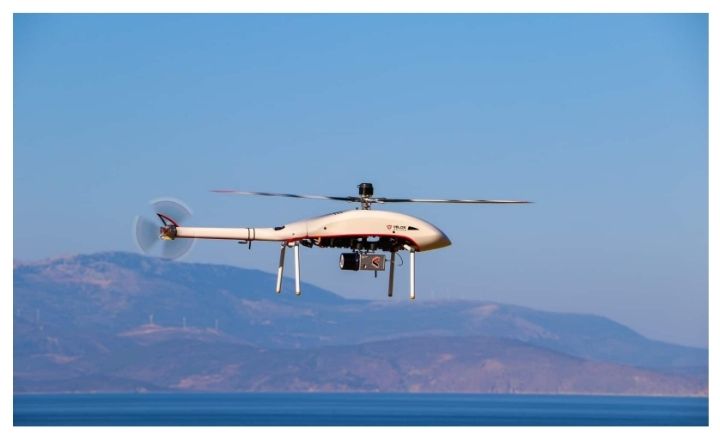

Multi-rotor
These are also called rotary-wing drones, are liked by many for their stability and ability to move quickly. They can hover and do precise movements better than fixed-wing drones. But, they have a shorter flight time of less than an hour because they use a lot of energy to keep multiple rotors working simultaneously.
Fixed-wing
They are commonly used to map large areas because they fly efficiently. These drones use air and force to stay in the air for a long time. They have wings like airplanes and need a big open area to take off and land. This makes them suitable for outdoor operations with plenty of space.
Fixed-wing Hybrid VTOL
Hybrid VTOL drones are special uncrewed aerial vehicles that can take off vertically like helicopters and fly like airplanes. They are helpful for tasks like surveillance, mapping, and deliveries. These drones have stabilization systems, allowing them to hover like quadcopters and fly efficiently.
According To Their Sizes
Drones come in a variety of sizes, each designed for specific tasks and purposes:
| Size | Very small drones | Small drones | Medium drones | Large drones |
| Length | 150mm (15cm, 6 inches) or less | Up to 300mm (12 inches) | 300-1200mm (12 inches – 4 feet) | 120cm (4 feet) and up |
| Propeller diameter | 51mm (2 inches) or less | 76-152mm (3-6 inches) | 150-640 mm (6-25 inches) | 64 cm (25 inches) and up |
| Weight | 200 grams (0.2kg, 0.44lbs) or less | 200-1000 grams (0.44-2.2lbs) | 1-20kg (2.2-44 pounds) | 20kg (44 pounds) and up |
| Use | Get footage of hard to reach places | Recreation and photography | Amateur photography | Enemy detection and combat capabilities |
Tiny Drones (Nano)
Nano drones are tiny uncrewed aerial vehicles that are changing how surveillance and reconnaissance are done. They can fly in tight spaces quietly and without being easily seen on the radar or by people.
Small
These are bigger than micro drones but are still compact and light. They are versatile and have fixed wings for a simple design. They can be thrown into the air quickly, making them suitable for indoor spaces. They can take high-quality photos and videos.
Medium
These drones are in between small and large drones. They are bigger and heavier, needing at least two people to lift them. They can fly longer and are more stable, making them suitable for professional uses like photography.
Large
Giant drones are like small aircraft and are used mainly for military purposes. They are sometimes replacing fighter jets and offer fast enemy detection and combat abilities.

According To Motors
There are generally two drone types classified according to motors:
| Drone motor | Brushless drone motors | Brushed drone motors |
| Pros | 1. Longer lifespan 2. Reduced heat generation 3. Better speed and torque due to the absence of brushes, because brush friction increases with speed 4. Less noise | 1. Inexpensive 2. Replaceable brushes for intended life 3. No speed controller is required for fixed speed 4. Can be made in a small package |
| Cons | Require an electronic controller | Operate at slower speed |
Brushed Drone Motors
Brushed drone motors are commonly used in drones for their simplicity and affordability. These motors are connected to gears that reduce speed and power output. They come in different sizes to fit various drone designs. Brushed motors are easy to maintain and repair, making them popular among beginners.
Brushless Drone Motors
Brushless drone motors are known for their efficiency and reliability. They require less maintenance than brushed motors because they don’t have brushes in contact with the rotor. This design leads to smoother operation and less wear and tear, resulting in a longer lifespan for the motor.
According To Their Payload Capacity
There are various drone types available in the market today, each designed with specific payload capacities to meet different needs and requirements:
| Drone type | Featherweight drones | Lightweight drones | Middleweight drones | Heavy-lift drones |
| Weight | Less than 11 grams (0.011 kg) | 200-1000 g (0.2-1 kg) | 1-600 kg (2.20-1323 lb) | More than 160 kg |
| Payload capacity | 4 grams to 100 grams (0.004 to 0.1 kg) | 150-270 g (0.15-0.27 kg) | 400-1460 grams (0.4-1.46 kg) | More than 1,000 kg |
| Use | Military surveillance | Recreation and photography | Professional applications and aerial photography | Civil applications such as drone deliveries or filmmaking |
Featherweight
They also called nanoscale drones, are becoming popular because they are small and light. They weigh as little as 11 grams, making them suitable for carrying small cameras or sensors. Despite their small size, these drones are agile and can move quickly in tight spaces.
Lightweight
These are famous for being versatile and easy to use. They usually weigh between 200 and 1000 grams and are great for hobbyists, photographers, and professionals in different industries. Even though they are small, lightweight drones come in various designs with varying payload capacities.
Middleweight
These drones, which weigh between 1-600 kg, are versatile and can carry different payloads. These drones are used in agriculture, surveying, and search and rescue missions because they can carry moderate-sized equipment while staying stable in flight.
Heavy Lift
They are essential for military operations because they can carry payloads of over 160 kg. They are used for logistical support, transporting heavy equipment, and strategic missions. Some heavy-lift drones can hold over 1,000 kilograms, showing the innovation in this field.

According To Their Power Sources
Drones come in various types based on their power sources, each offering unique capabilities and applications:
| Power source | Battery-powered drones | Hydrogen fuel cell drones | Gasoline-powered drones | Solar drones |
| Pros | 1. Lightweight 2. Ability to store decent amounts of energy 3. High discharge rates | 1. Resourceful 2. Lightweight 3. Longer flight time 4. Refuels quickly | 1. Refuel on demand 2. Easier to repair and maintain long term 3. Higher flight speed | 1. Easily spot hard to reach areas 2. Affordable Lightweight |
| Cons | 1. Short lifespan 2. Mistreat them and they can start a fire 3. Use up energy fast | A lot of heat is generated | 1. Produce more noise 2. Large size | Limited flight time |
Battery-powered
These drones use three common types of batteries. Lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries are popular among drone enthusiasts for their lightweight design and high energy density, allowing longer flight times and better performance.
NiMH batteries are stable and long-lasting, making them a good choice for beginner pilots or those looking for a cost-effective option. Nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries are less common in modern drones due to safety concerns and lower capacity but still have uses in specialized drone applications.
Hydrogen Fuel Cell
They are a new advancement in UAV technology, offering unique capabilities and advantages. Unlike traditional drones with internal combustion engines, hydrogen fuel cell drones are more efficient at high altitudes because they can maintain consistent power output regardless of air pressure changes.
This makes them well-suited for aerial surveillance, environmental monitoring, and crop analysis in mountainous or remote areas where other drones may struggle.
Gasoline-powered
These are popular for large drones because gasoline is efficient and affordable as fuel. These drones can carry heavy loads for extended periods, making them ideal for agriculture, surveying, and aerial photography applications. Gasoline-powered drones can operate in remote locations where recharging options are limited.
Solar
These are innovative, uncrewed aerial vehicles that use solar power to operate sustainably. Equipped with solar panels, these drones can convert sunlight into energy.
According To Drone Range
Drones come in various types based on their range capabilities, which can significantly impact their applications:
| Drone range | Very close-range drones | Close-range drones | Short-range drones | Mid-range drones | Long-range drones |
| Flight distance | 5 km | up to 50 km | up to 150 km | 644 km | More than 644 km |
| Flight time | 1 hour | 1-6 hours | 8-12 hours | 24 hours | More than 24 hours |
| Use | Recreation | 1. Military surveillance 2. Reconnaissance | 1. Large-scale surveillance 2. Mapping and surveying 3. Utility inspection | 1. Surveillance 2. Safety | 1. Coastline mapping 2. Landscape travel footage 3. Photogrammetry |
Very Close-range
They can be controlled within a range of 5 km from the operator. They are suitable for beginners and indoor use. These drones are popular among hobbyists and photographers for capturing close-up shots quickly. They generally operate within a limited distance of 50 km from the controller.
Close-range
They are smaller and lighter, suitable for short-range explorations or aerial photography close to the ground. They are commonly used for monitoring crops, surveying land, or capturing footage in tight spaces.
Short-range
They have a range of up to 150 km from the controller. They are popular among hobbyists and beginners for their ease of use and affordable price. These drones are great for capturing aerial shots and exploring nearby areas. They often come with basic camera capabilities for taking stunning photos or videos from above.

Mid-range
It can fly up to 400 miles (644 km) on a single charge. They are ideal for aerial photography, surveillance, and mapping missions.
Long-range
They are designed for extended flights and can travel well over 400 miles (644 km) in a single journey. They have advanced technology for stable flight paths even at significant distances from the operator.
According To Their Abilities And Equipment
Drones have become increasingly popular in recent years, with various types available to cater to different needs and requirements:
RTF
They are great for beginners and those who want a straightforward flying experience. They come ready to fly out of the box with minimal setup. They usually include controllers, batteries, and sometimes a camera.
Toy
These are popular with beginners and kids because they are easy to use and affordable. They have basic features like stabilization sensors and simple flight controls ranging from 100 to 200 feet. They are suitable for indoor flying and practicing flying skills.
Racing Drones
Racing or FPV drones are made for fast flying and agility. They have powerful motors and designs for high speeds and precise flying. FPV racing is a fun sport requiring skill and precision to fly through high-traffic obstacle courses.
GPS
They are changing the drone industry with their advanced GPS technology. They can fly precisely and navigate accurately by using GPS systems. These drones can do tasks on their own, like following set flight paths or staying in one spot. If their battery is low or they lose connection, they can return home safely.
Military
Military drones have changed a lot over the years and are now used in conflicts worldwide. Initially, they were used for spying, but now, they have w_ea_p_ons and are essential in modern warfare.
Photography And Videography
Camera drones have changed how we take amazing pictures and videos from unique angles. They have high-quality cameras that can record in HD, Full HD, or 4K for clear images. The camera is often on a stable mount for smooth footage.
Professional
These have special tools like sensors or thermal cameras for services such as mapping or surveillance. They provide detailed and accurate data for agriculture, construction, and search and rescue industries. These drones are making tasks more efficient and cost-effective.

Wrapping Up
Drones are very useful in many industries because they can do a lot of different things. They are used for taking pictures from the sky and helping with finding people in emergencies. There are different types of drones, like fixed-wing, multirotor, and single rotor, that are good for different jobs. In the future, drones will keep getting better and will change how we do things in farming, building, and emergencies. It’s important to use these new technologies to get the most out of what drones can do.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are there Regulations Regarding where Drones can be Flown?
Yes, there are strict regulations governing where drones can be flown to ensure safety and privacy concerns are addressed.
How Long do Drone Batteries typically last?
Drone battery life varies depending on the model but generally ranges from 15 minutes to 30 minutes per charge.
How can I Learn to Fly a Drone Safely and Legally?
It is recommended to take a drone piloting course or seek guidance from experienced pilots to learn how to operate a drone safely and comply with local laws and regulations.